Bare-metal x86-64 image
This page spiecifies how to create a bare-metal ERIKA3 RTOS image for x86-64. The following image can be used for running on Qemu or with Xen/KVM hypervisor.
This tutorial explains how to setup RT_Druid environment to compile ERIKA3 RTOS application and how to create an ERIKA3 bare-metal image running a simple application.
Contents
Bare-metal compiler set-up
Download the bare-metal toolchain available at this link http://erika-enterprise.com/download/erika3_x86_64_xtools.tar.gz and extract the downloaded archive.
The x-tool binary prefix will be used to set the x86_64 property named Gnu compiler prefix in the RT-Druid environment as explained in the next section. More in detail, let us suppose the bare-metal archive has been extracted in the home directory (i.e., /home/evidence). Then, the Gnu compiler prefix property assumes the following value: /home/evidence/x-tools/x86_64-unknown-elf/bin/x86_64-unknown-elf-.
RT-Druid set-up
In order to run RT-Druid on the platform, download the RT-Druid package from the download section of the ERIKA3 website. Then, extract the downloaded archive. In the following part of the tutorial, we refer to directory containing the extracted RT-Druid archive as $RTDRUID_DIR.
Launch the RT-Druid application as follows:
$ cd $RTDRUID_DIR $ ./eclipse
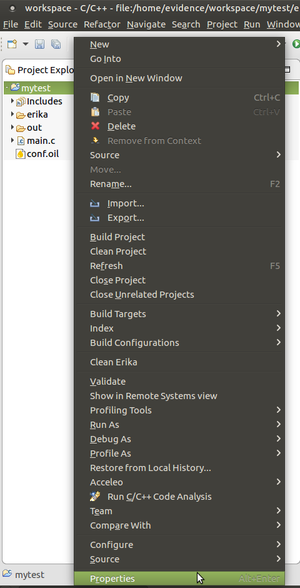
In order to enable the bare-metal compiler tool, set the Gnu compiler prefix property. RT-Druid allows to set these variables also from within Eclipse. Just press the right mouse button on the Eclipse project and select Properties as shown in the following figure.
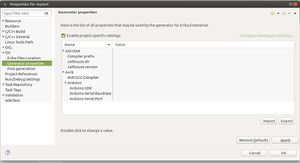
Then, select Generator properties, enable project specific settings (as shown in the next figure), and set the desired value for the X86_64 property named Gnu compiler prefix.
Note that RT-Druid allows to set these variables for a single project by just pressing the right mouse button on the Eclipse project and selecting Properties).
Simple application
As ERIKA3 application we consider the simple "helloworld" application consisting of two tasks printing on the serial interface.
- Run the RT-Druid tool $ cd $RTDRUID_DIR $ ./eclipse
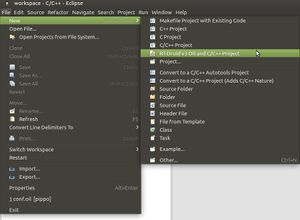
- Create a new project by clicking on
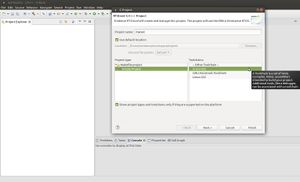
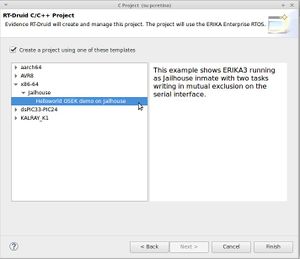
New→RT-Druid v3 Oil and C/C++ Projectas shown in the next Figure: - Name the new project (e.g.,
mytest) as shown in the next Figure: - Check the box for using an existing template and select
x86-64→Helloworld OSEK demoas shown in the next Figure: - Eclipse will then show the new project, and RT-Druid will generate the configuration files, as shown in the next Figure:
- Modify the configuration file
conf.oilby settings the following parameters:- The parameter
PLATFORMdefines the supported platform (default value isJAILHOUSE). In order to generate the bare-metal image set the parameter as follows:PLATFORM = BARE. - The parameter
INT_CONTROLLERdefines the supported interrupt controller and the values areAPICorX2APIC(default value isX2APIC). APIC ("Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller") is the updated Intel standard for the older PIC. It is used in multiprocessor systems and is an integral part of all recent Intel (and compatible) processors. Its variant, referred to as X2APIC, is the most recent generation of the Intel's programmable interrupt controller and has been introduced with the Nehalem microarchitecture in November 2008. - In case of X2APIC mode, the parameter
X2APIC_MODEdefines whether the X2APIC is operating in the TSC deadline mode or not. The parameter is under theINT_CONTROLLER = X2APICparameter and the values areTSC_DEADLINEandNO_TSC_DEADLINE(default value isTSC_DEADLINE).
- The parameter
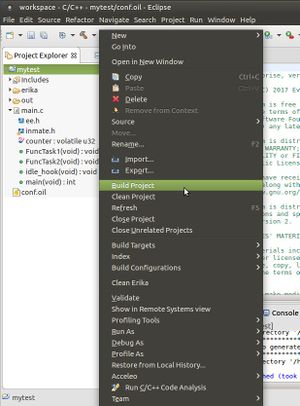
- Click with the right mouse key on the project and select
Build projectas shown in the next Figure:
The resulting elf file, contained in $ECLIPSE_WORKSPACE/mytest/out will be used to build the ERIKA3 bare-image as explained in the following section.
Build the ERIKA3-image
The bootable ERIKA3 image is a bootable GRUB2 image, where GRUB2 for i386-pc is responsible for loading the elf image containing ERIKA3 RTOS and application.
First of all, check whether there is GRUB package installed and, in case so, check whether it is GRUB2 for i386-pc by launching the following command:
$ dpkg --get-selections | grep grub
and checking whether the output contains the line grub-pc.
In case there is no grub-pc, you need to build to build GRUB2 from scratch as follows:
$ git clone git://git.savannah.gnu.org/grub.git $ cd grub $ git checkout grub-2.02-rc2 -b grub-pc-for-erika ## Latest tested Grub version $ ./autogen.sh $ ./configure --disable-werror --prefix=$GRUBDIR $ make && make install
where $GRUBDIR is the GRUB2 installation directory (as for example, $HOME/grub). Then, in order to launch a grub command (i.e., get the grub-mkrescue version), use the chosen GRUB2 installation directory as prefix, as shown below:
$ $GRUBDIR/bin/grub-mkrescue -V
In case there is already grub-pc, use the correspond commands from command line, as shown below:
$ grub-mkrescue -V
Then, create the ISO folder as follows:
$ mkdir -p iso/boot/grub
Create the grub.cfg file in iso/boot/grub:
set timeout=0
set default=0
menuentry "erika_os" {
multiboot /boot/erika.elf
boot
}
Then, copy the erika.elf file into iso/boot. Launch the grub-mkrescue command to create the multi-boot image.
$GRUBDIR/bin/grub-mkrescue -o erika3.iso iso
Note that grub-mkrescue command requires xorriso package.