Difference between revisions of "FatFS"
(Created page with "= Introduction = FatFs is a tiny library which provides FAT/exFAT support for small embedded systems. File system functionalities are separated from the disk I/O layer and ar...") |
(→Providing a file system mkfs/dd) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
=== Providing a file system with FatFS built for Linux === | === Providing a file system with FatFS built for Linux === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
TBD | TBD | ||
Revision as of 13:48, 8 March 2019
Contents
Introduction
FatFs is a tiny library which provides FAT/exFAT support for small embedded systems.
File system functionalities are separated from the disk I/O layer and are easy to configure by enabling/disabling options.
The stack support will be provided in the next release of Erika with a memory driver which basically exports a portion of memory as a block device.
The following sections describe how to use use a subset of basic functionalities of FatFs.
Erika/FatFS demo on Jetson TX2 with Jailhouse Hypervisor (aarch64)
This demo shows how to handle directories/files on a FAT file system on Erika Enterpries v3 running as a Jailhouse inmate on Jetson TX2 board:
- Download the FatFs library as archive from the Download section on http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html or simply clone the Git reposity from https://github.com/RIOT-OS/FatFS.git
- In the FatFs downloaded sources enable the Long Filename Support and the Mkfs function (in
/full/paty/FatFS/source/ffconf.henable the defines#define FF_USE_LFN 1and#define FF_USE_MKFS 1) - Set the build environment as described in Nvidia Jetson TX1 and TX2 (cross-toolchain, Jetson platform setup, Jailhouse cross-compiling)
- Run the RT-Druid tool
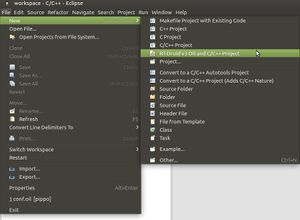
- Create a new project by clicking on
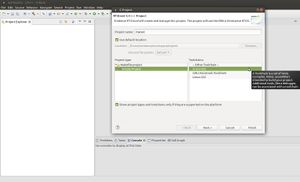
New→RT-Druid v3 Oil and C/C++ Projectas shown in the next Figure: - Name the new project (e.g.,
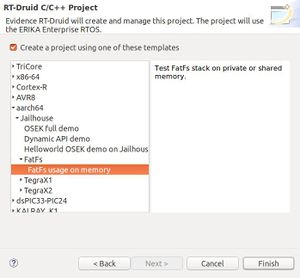
mytest) and select the Cross-GCC as shown in the next Figure: - Check the box for using an existing template and select
aarch64→Jailhouse→FatFs→FatFs usage on memoryas shown in the next Figure: - Right click the project and select
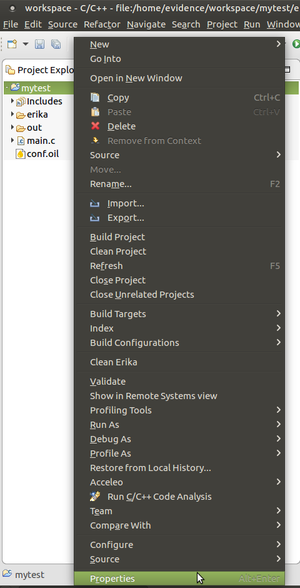
Propertiesas shown in the following Figure: - Click
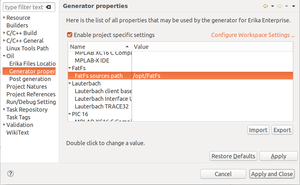
Oil→Generator properties, enable project specific settings and specify the directory containing the FatFs library for ERIKA3: - Configure the RT-Druid as described in Nvidia Jetson TX1 and TX2#RT-Druid set-up
Creating a private FAT file system on Erika
When the #define EE_MEM_LOCAL is enabled in main.c, Erika will perform such actions:
- Before starting OS, will:
- inizialize the
fmemdriver - create a FAT file system on an array located in
.datasection of the executable - create the directory
test - create the file
erika.txtin the directorytest
- inizialize the
- The
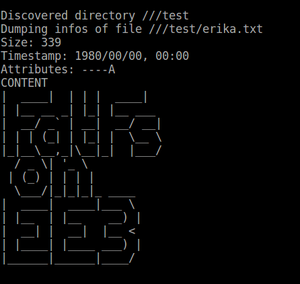
Task1will dump the directories and files content ( output should look like this):
Sharing a FAT file system with Linux
When the #define EE_MEM_LOCAL is disabled in main.c, Erika expects to find a valid FAT file system
at the address location #define memory (const void*)(0x274800000).
This address represents the start of a shared memory region between Erika and Linux where the latter must provide a valid file system (see next subsections).
After proper fmem initialization with the shared memory address, Erika will perform the same actions of directory/file creation described in the previous example.
Please note that the memory region must be mapped into the inmate address space through the map_range function.
Furthermore Jailhouse should be aware of this shared region. This is achieved by putting in both the root cell and inmate cell the section:
{
.phys_start = 0x274800000,
.virt_start = 0x274800000,
.size = 0x80000,
.flags = JAILHOUSE_MEM_READ | JAILHOUSE_MEM_WRITE
| JAILHOUSE_MEM_ROOTSHARED,
},
NOTE: configurations sources are jetson-tx2.c and jetson-tx2-demo.c located in the folder configs/arm64 of the Evidence Jailhouse repository cloned from https://github.com/evidence/linux-jailhouse-jetson.git. Don't forget to increase the struct jailhouse_memory mem_regionsnumber at the beginning of the files.
After configurations' update, they must be rebuilt (follow instruction in the README.md of the same repository).
Providing a file system with FatFS built for Linux
TBD